Business object properties define the information that is carried on a business object. The properties section is on the top left of the Business Object Page:
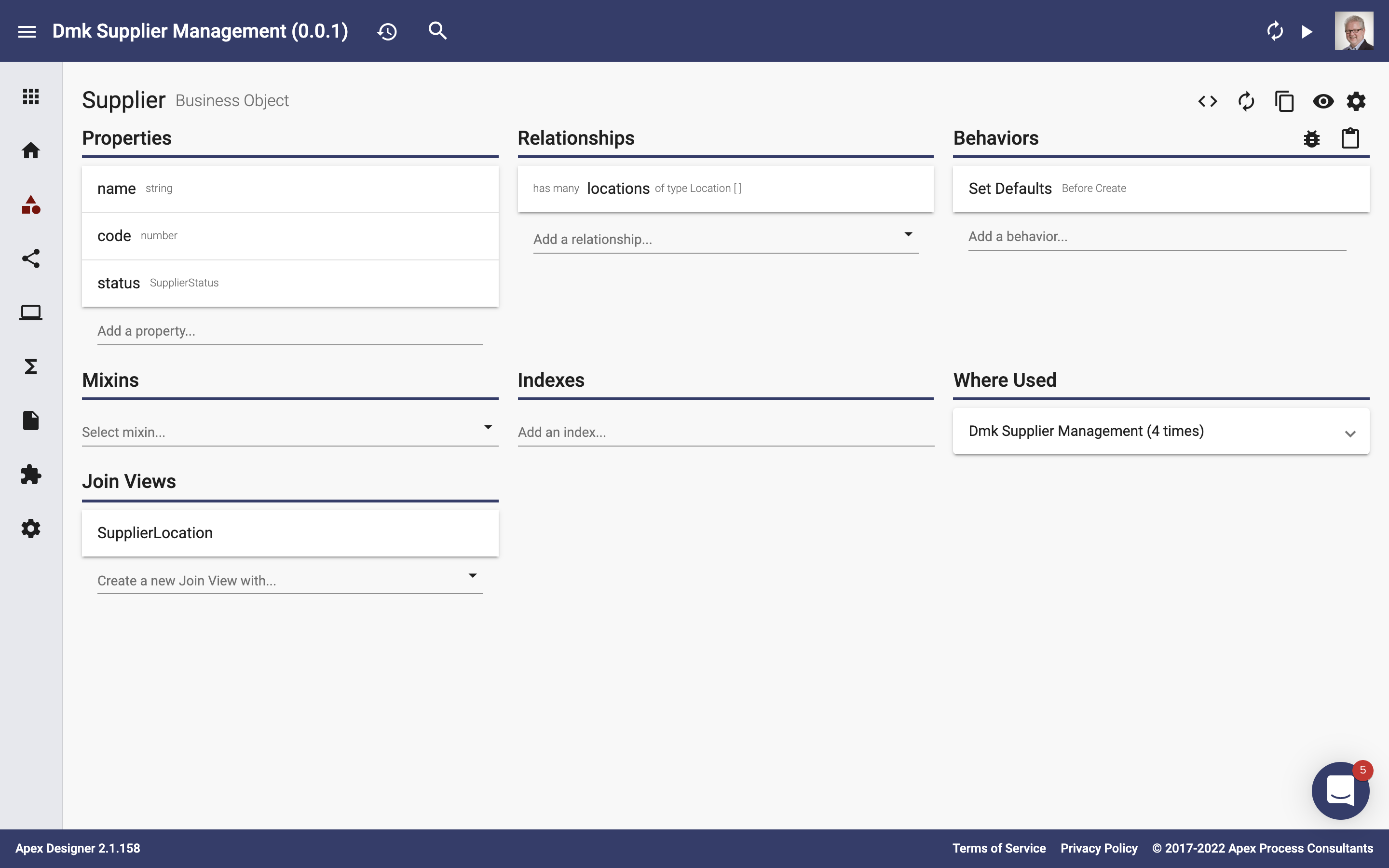
Adding Properties
To add a property, enter the name and optionally part of the type in the "Add a property..." field:
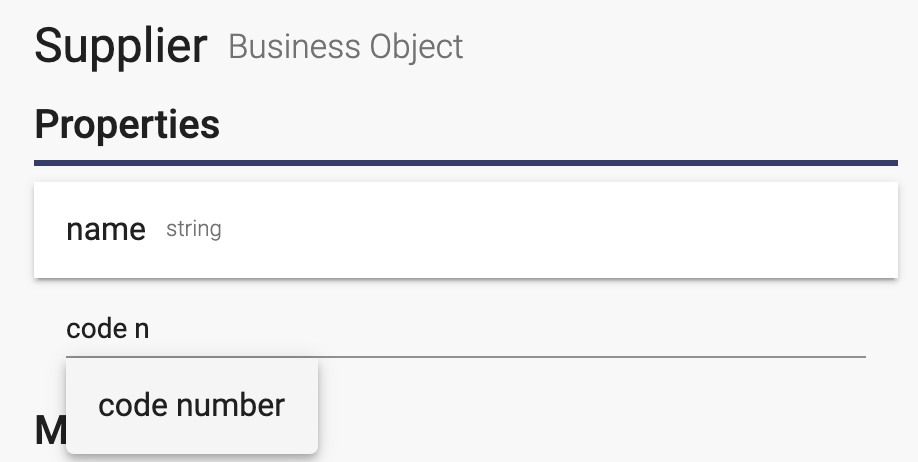
Property Dialog
Click on a property to open the property dialog:
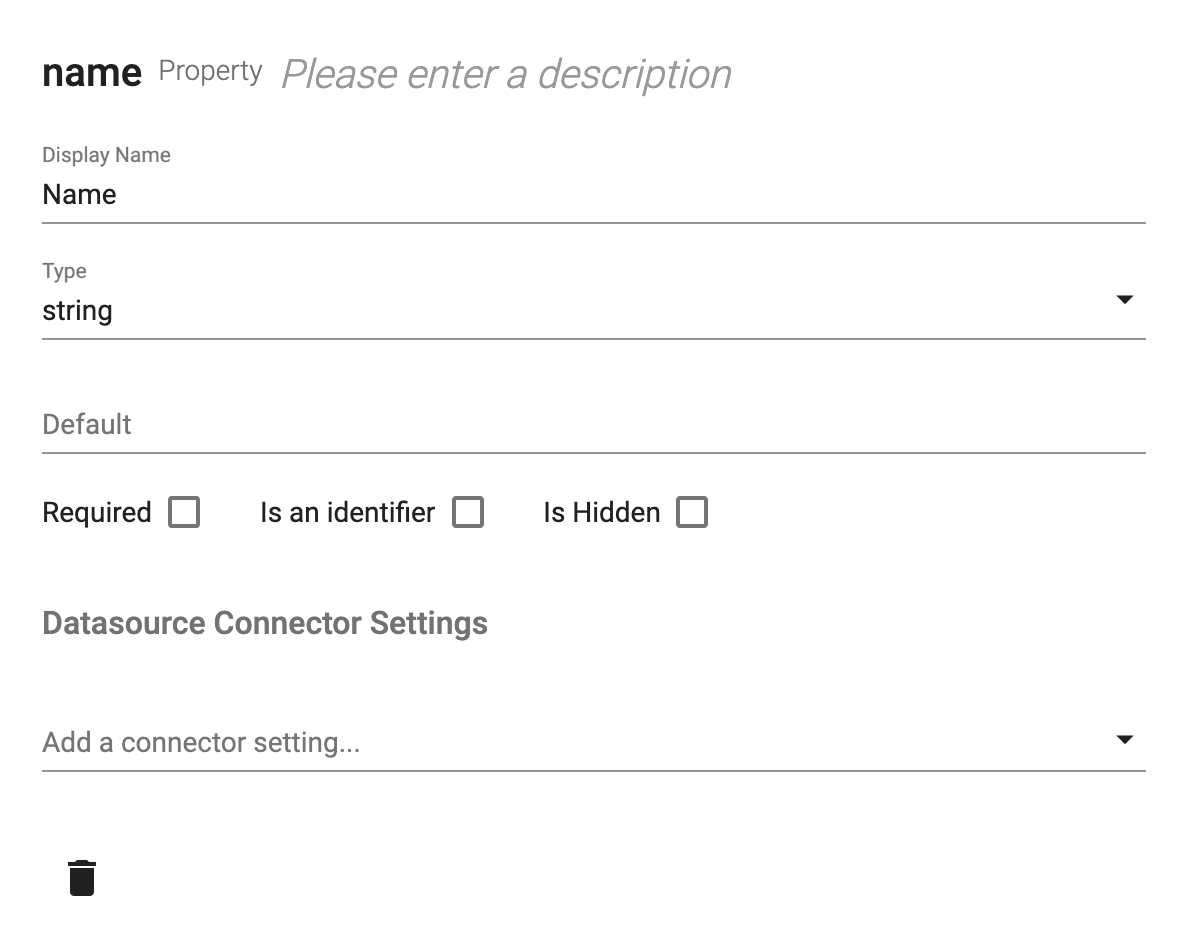
Starting from the top, here are details about the dialog contents:
- You can edit the Name and Description inline on the first line.
- The Display Name is used as the default field label or column name.
- The Type field lets you select a native type (e.g. string) or a base type (e.g. Supplier Status)
- You can specify a default value.
- Checking the "Required" checkbox will make fields required and set the underlying database column to not null (if applicable).
- Checking the "Is an Identifier" checkbox will make this property the unique identifier for the business object (this is only used in very special cases used because Apex Designer implicitly adds an "id" property to all business objects).
- Checking the "Is Hidden" checkbox will exclude this from the fields on a page and the columns on a table (unless you explicitly include it).
- Datasource Connector Settings allows you to override default column types. A typical example is configuring a currency property as a numeric column with 4 decimal places of precision:

- You can delete the business object by clicking the delete icon button.
Property Order
You can reorder the properties by dragging and dropping them. The property order defines the default order for fields on a page or columns in a table.
No Complex Properties
Properties can only be a native types (e.g. string) or a base type (e.g. SupplierStatus). It cannot be another business object with properties. For example, Supplier can't have an "address" property of type Address which in turn has street, city, state and zip properties. These cases are handled using Business Object Relationships instead.